Self-Care
Health Conditions To Be Aware Of Over Age 55
Published
12 months agoon

Shutterstock
Embarking on the journey of aging is like unlocking the chapters of a novel, each page revealing new facets of our health story. Just as the plot thickens, our bodies undergo transformations, and with that comes the possibility of encountering various medical conditions. These can take center stage, adding complexity to our golden years.
Let’s explore some medical conditions that become more common as we age.
Cardiovascular Disease
Shutterstock
- What is it? A broad term encompassing conditions affecting the heart and blood vessels, such as coronary artery disease. Can Develop over time due to factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and lifestyle choices.
- Symptoms can include: Chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue.
- When can it develop? Risk increases with age, often starting to manifest in middle to older age, but lifestyle factors contribute.
Macular Degeneration
Shutterstock
- What is it? Deterioration of the macula in the eyes, leading to vision loss.
- Symptoms can include: Blurred or distorted central vision.
- When can it develop? Risk increases with age, often starting to manifest in middle to older age, but lifestyle factors contribute.
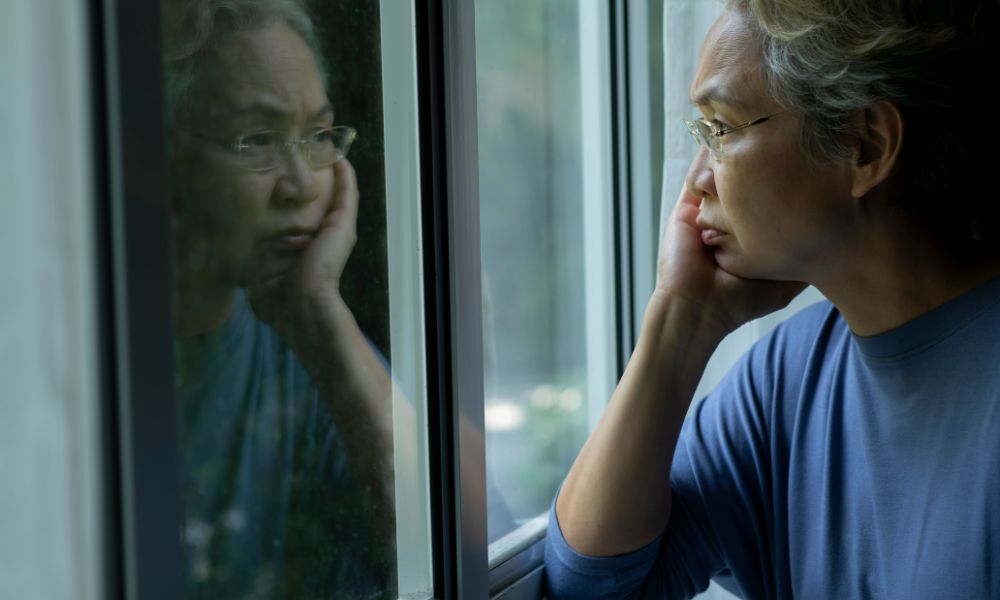
Depression

Shutterstock
- What is it? A mood disorder characterized by persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and a lack of interest or pleasure in activities.
- Symptoms can include: Changes in appetite and sleep patterns, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
- When can it develop? Often first manifests during adolescence or early adulthood.
Type 2 Diabetes
Shutterstock
- What is it? A metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels.
- Symptoms can include: Increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue.
- When can it develop? Typically diagnosed in adulthood, but lifestyle factors can contribute to earlier onset.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Shutterstock
- What is it? Autoimmune disorder causing joint inflammation and deformities.
- Symptoms can include: Joint pain, swelling, and morning stiffness.
- When can it develop? Typically starts between ages 30 and 60, but it can occur at any age.
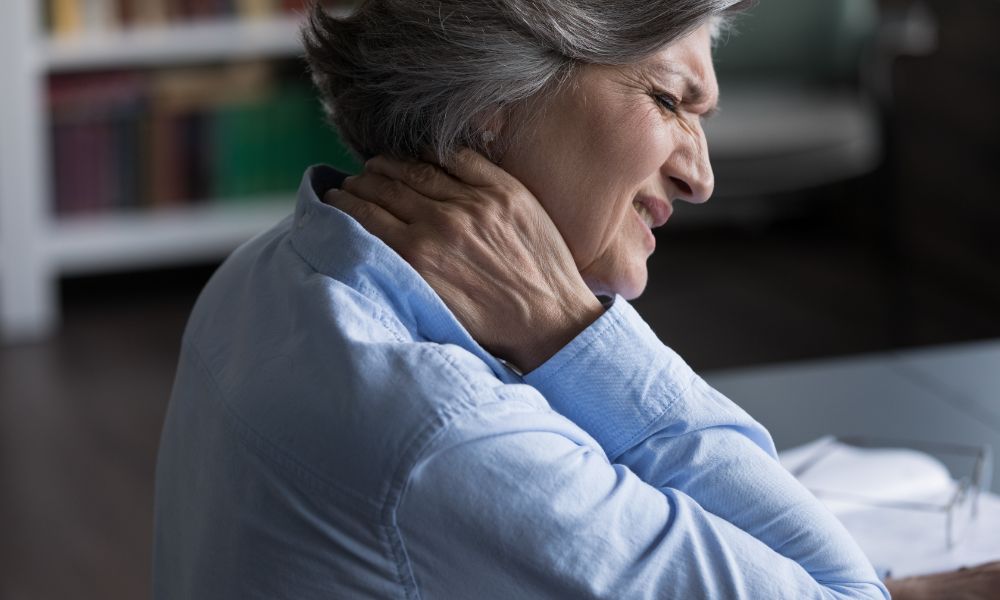
Fibromyalgia

Shutterstock
- What is it? Chronic pain syndrome characterized by widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness in localized areas.
- Symptoms can include: Heightened sensitivity to pressure, sleep disturbances, cognitive issues, and headaches.
- When can it develop? Commonly diagnosed in adults, particularly between the ages of 30 and 60, but can develop at any age.
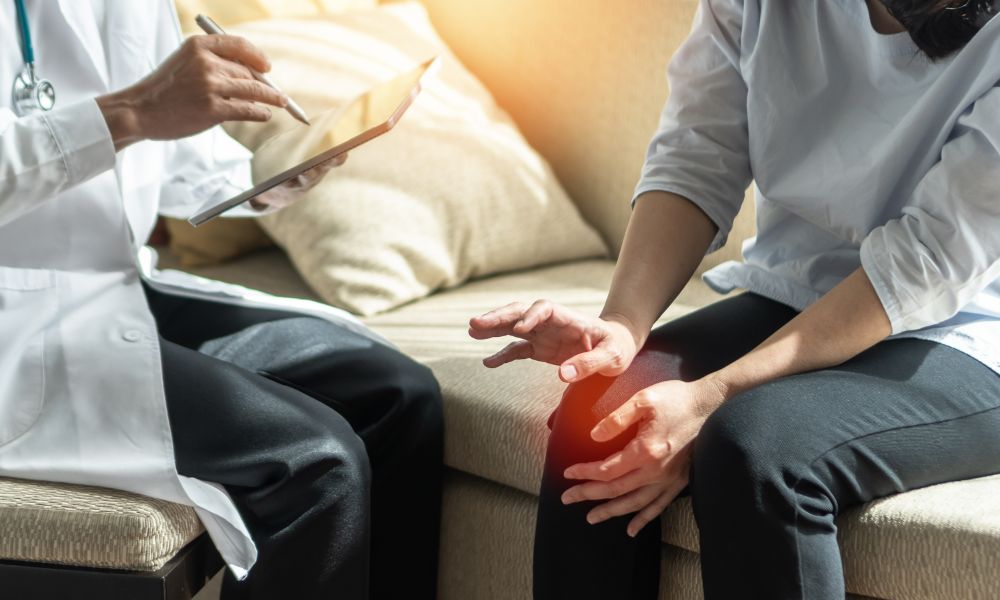
Osteoporosis

Shutterstock
- What is it? Reduction in bone density, making bones brittle which can lead to increased fragility and susceptibility to fractures.
- Symptoms can include: Fractures, loss of height, and stooped posture.
- When can it develop? Bone density loss starts in midlife.
High Blood Pressure
Shutterstock
- What is it? Also known as Hypertension. A condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels, exerting increased force on the walls of the arteries. Hypertension can lead to severe health complications if left untreated.
- Symptoms can include: Often asymptomatic, but severe causes may include persistent headaches, shortness of breath and dizziness.
- When can it develop? High blood pressure can develop at any age, the risk increases with age, making it more common in middle-aged and older adults.
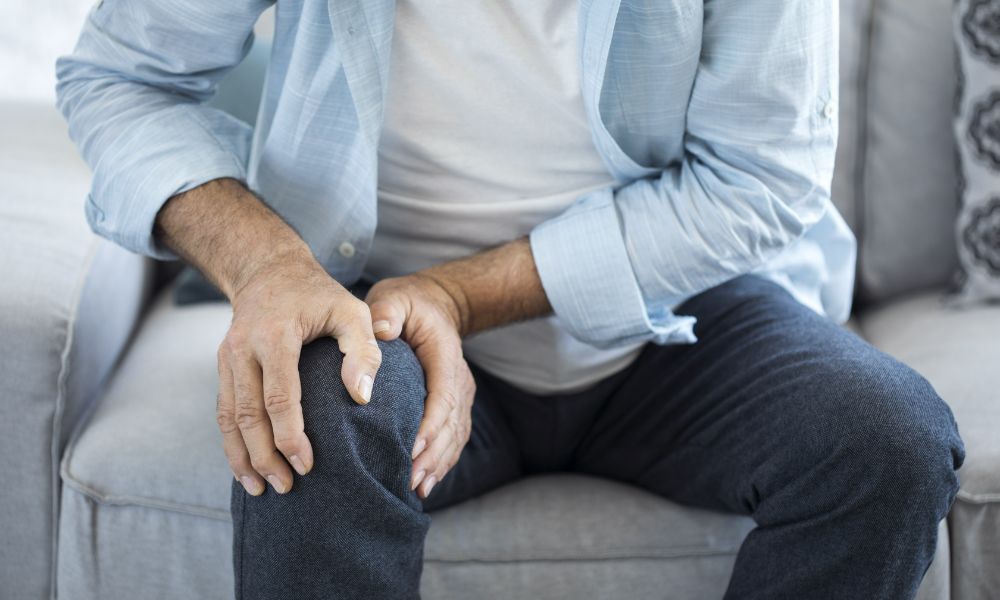
Osteoarthritis

Shutterstock
- What is it? Degeneration of joint cartilage that tends to worsen with age, affecting mobility.
- Symptoms can include: Joint pain, swelling, and reduced range of motion.
- When can it develop? Common in older adults, but joint wear and tear can begin earlier, especially with joint injuries.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Shutterstock
- What is it? A progressive lung disease characterized by airflow limitation, making it challenging to breathe. Common forms of COPD include chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
- Symptoms can include: Shortness of breath, chronic cough, and wheezing.
- When can it develop? Usually diagnosed in middle-aged or older adults, often linked to smoking.
High Cholesterol

Shutterstock
- What is it? A condition characterized by elevated levels of cholesterol in the blood, specifically high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad” cholesterol.
- Symptoms can include: Symptoms of high cholesterol are usually absent, making it a silent condition.
- When can it develop? While cholesterol levels can start to rise in childhood, the risk increases with age, and routine screenings are recommended for adults starting around age 20 to monitor and manage cholesterol levels effectively.
Chronic Kidney Disease

Shutterstock
- What is it? Gradual loss of kidney function, leading to kidney damage.
- Symptoms can include: Fatigue, swelling, and changes in urination.
- When can it develop? More common in older adults, often associated with other conditions like diabetes and hypertension.
Alzheimer’s Disease

Shutterstock
- What is it? Progressive neurodegenerative disorder leading to memory loss and cognitive decline.
- Symptoms can include: Memory loss, confusion, or changes in behavior.
- When can it develop? More common in older adults, often diagnosed after age 65, but early-onset forms exist.
Cancer
Shutterstock
- What is it? Uncontrolled cell growth with the potential to invade other tissues. Various forms of cancer, including lung, breast, and colon, can develop over time.
- Symptoms can include: Vary depending on the type of cancer, but may include lumps, changes in bowel habits and unexplained weight loss.
- When can it develop? Cancer risk increases with age, and specific types may manifest at different stages of life.
Pneumonia

Shutterstock
- What is it? Respiratory infection characterized by inflammation of the air sacs in the lungs, often caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens.
- Symptoms can include: Persistent cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and fever; signaling an infection affecting the lungs.
- When can it develop? Can occur at any age, it poses a higher risk for older adults, young children, and individuals with weakened immune systems.
Conclusion

Shutterstock
As we age in life it’s possible these medical conditions may play supporting roles, but with knowledge, awareness, and proactive care, individuals can script a tale of resilience, well-being, and a life well-lived.